9.5 KiB
9.5 KiB
| id | title | sidebar_position | data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 控制语句 | 控制语句 | 3 | 2022年4月28日 |
条件语句
if 语句
如果布尔表达式为 true,则 if 语句内的代码块将被执行。如果布尔表达式为 false,则 if 语句结束后的第一组代码(闭括号后)将被执行。
C 语言把任何非零和非空的值假定为 true,把零或 null 假定为 false。
if (boolean_expression)
{
// 如果布尔表达式为真将执行的语句
}
// 实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 10;
// 使用 if 语句检查布尔条件
if( a < 20 )
{
// 如果条件为真,则输出下面的语句
cout << "a 小于 20" << endl;
}
cout << "a 的值是 " << a << endl;
return 0;
}
// 输出
a 小于 20
a 的值是 10
if...else 语句
如果布尔表达式为 true,则执行 if 块内的代码。如果布尔表达式为 false,则执行 else 块内的代码。
if (boolean_expression)
{
// 如果布尔表达式为真将执行的语句
}
else
{
// 如果布尔表达式为假将执行的语句
}
// 实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 100;
// 检查布尔条件
if( a < 20 )
{
// 如果条件为真,则输出下面的语句
cout << "a 小于 20" << endl;
}
else
{
// 如果条件为假,则输出下面的语句
cout << "a 大于 20" << endl;
}
cout << "a 的值是 " << a << endl;
return 0;
}
// 输出
a 大于 20
a 的值是 100
if...else if 多分支语句
一个 if 语句后可跟一个可选的 else if...else 语句,这可用于测试多种条件。
当使用 if...else if...else 语句时,以下几点需要注意:
- 一个 if 后可跟零个或一个 else,else 必须在所有 else if 之后。
- 一个 if 后可跟零个或多个 else if,else if 必须在 else 之前。
- 一旦某个 else if 匹配成功,其他的 else if 或 else 将不会被测试。
// 语法
if(boolean_expression 1)
{
// 当布尔表达式 1 为真时执行
}
else if( boolean_expression 2)
{
// 当布尔表达式 2 为真时执行
}
else if( boolean_expression 3)
{
// 当布尔表达式 3 为真时执行
}
else
{
// 当上面条件都不为真时执行
}
// 实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 100;
// 检查布尔条件
if( a == 10 )
{
// 如果 if 条件为真,则输出下面的语句
cout << "a 的值是 10" << endl;
}
else if( a == 20 )
{
// 如果 else if 条件为真,则输出下面的语句
cout << "a 的值是 20" << endl;
}
else if( a == 30 )
{
// 如果 else if 条件为真,则输出下面的语句
cout << "a 的值是 30" << endl;
}
else
{
// 如果上面条件都不为真,则输出下面的语句
cout << "没有匹配的值" << endl;
}
cout << "a 的准确值是 " << a << endl;
return 0;
}
// 输出
没有匹配的值
a 的准确值是 100
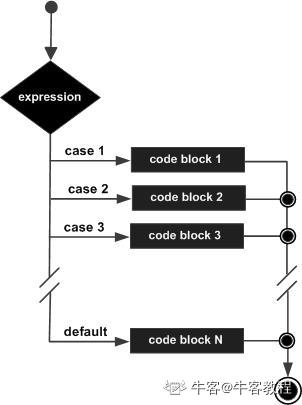
switch 多分支语句
一个 switch 语句允许测试一个变量等于多个值时的情况。每个值称为一个 case,且被测试的变量会对每个 switch case 进行检查。
语法
switch(expression){
case constant-expression :
statement(s);
break; // 可选的
case constant-expression :
statement(s);
break; // 可选的
// 您可以有任意数量的 case 语句
default : // 可选的
statement(s);
}
switch 语句必须遵循下面的规则:
- switch 语句中的 expression 必须是一个整型或枚举类型,或者是一个 class 类型,其中 class 有一个单一的转换函数将其转换为整型或枚举类型。
- 在一个 switch 中可以有任意数量的 case 语句。每个 case 后跟一个要比较的值和一个冒号。
- case 的 constant-expression 必须与 switch 中的变量具有相同的数据类型,且必须是一个常量或字面量。
- 当被测试的变量等于 case 中的常量时,case 后跟的语句将被执行,直到遇到 break 语句为止。
- 当遇到 break 语句时,switch 终止,控制流将跳转到 switch 语句后的下一行。
- 不是每一个 case 都需要包含 break。如果 case 语句不包含 break,控制流将会 继续 后续的 case,直到遇到 break 为止。
- 一个 switch 语句可以有一个可选的 default case,出现在 switch 的结尾。default case 可用于在上面所有 case 都不为真时执行一个任务。default case 中的 break 语句不是必需的。
流程图
实例
// 实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
char grade = 'D';
switch(grade)
{
case 'A' :
cout << "很棒!" << endl;
break;
case 'B' :
case 'C' :
cout << "做得好" << endl;
break;
case 'D' :
cout << "您通过了" << endl;
break;
case 'F' :
cout << "最好再试一下" << endl;
break;
default :
cout << "无效的成绩" << endl;
}
cout << "您的成绩是 " << grade << endl;
return 0;
}
// 输出
您通过了
您的成绩是 D
循环语句
while 循环语句
// 语法
while(condition)
{
statement(s);
}
// 实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 10;
// while 循环执行
while( a < 20 )
{
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
a++;
}
return 0;
}
// 输出
a 的值: 10
a 的值: 11
a 的值: 12
a 的值: 13
a 的值: 14
a 的值: 15
a 的值: 16
a 的值: 17
a 的值: 18
a 的值: 19
do...while 循环语句
do...while 循环与 while 循环类似,但是 do...while 循环会确保至少执行一次循环。
// 语法
do
{
statement(s);
}while( condition );
// 实例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 10;
// do 循环执行
do
{
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
a = a + 1;
}while( a < 20 );
return 0;
}
// 输出
a 的值: 10
a 的值: 11
a 的值: 12
a 的值: 13
a 的值: 14
a 的值: 15
a 的值: 16
a 的值: 17
a 的值: 18
a 的值: 19
for 循环语句
for 循环允许您编写一个执行特定次数的循环的重复控制结构
- init 会首先被执行,且只会执行一次。这一步允许您声明并初始化任何循环控制变量。您也可以不在这里写任何语句,只要有一个分号出现即可。
- 接下来,会判断 condition。如果为真,则执行循环主体。如果为假,则不执行循环主体,且控制流会跳转到紧接着 for 循环的下一条语句。
- 在执行完 for 循环主体后,控制流会跳回上面的 increment 语句。该语句允许您更新循环控制变量。该语句可以留空,只要在条件后有一个分号出现即可。
- 条件再次被判断。如果为真,则执行循环,这个过程会不断重复(循环主体,然后增加步值,再然后重新判断条件)。在条件变为假时,for 循环终止。
for ( init; condition; increment )
{
statement(s);
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// for 循环执行
for( int a = 10; a < 20; a = a + 1 )
{
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
}
return 0;
}
// 输出
a 的值: 10
a 的值: 11
a 的值: 12
a 的值: 13
a 的值: 14
a 的值: 15
a 的值: 16
a 的值: 17
a 的值: 18
a 的值: 19
跳转语句
break 语句
- 当 break 语句出现在一个循环内时,循环会立即终止,且程序流将继续执行紧接着循环的下一条语句。
- 它可用于终止 switch 语句中的一个 case。
break;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 10;
// do 循环执行
do
{
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
a = a + 1;
if( a > 15)
{
// 终止循环
break;
}
}while( a < 20 );
return 0;
}
continue 语句
C++ 中的 continue 语句有点像 break 语句。但它不是强迫终止,continue 会跳过当前循环中的代码,强迫开始下一次循环。
continue;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 10;
// do 循环执行
do
{
if( a == 15)
{
// 跳过迭代
a = a + 1;
continue;
}
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
a = a + 1;
}while( a < 20 );
return 0;
}
goto 语句
goto 语句允许把控制无条件转移到同一函数内的被标记的语句。
在任何编程语言中,都不建议使用 goto 语句。因为它使得程序的控制流难以跟踪,使程序难以理解和难以修改。
goto label;
..
.
label: statement;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
int a = 10;
// do 循环执行
LOOP:do
{
if( a == 15)
{
// 跳过迭代
a = a + 1;
goto LOOP;
}
cout << "a 的值:" << a << endl;
a = a + 1;
}while( a < 20 );
return 0;
}
return 语句
返回语句